Learning about different pregnancy complications can help you monitor yourself and thus use your discernment to understand whether or not a particular symptom your are experiencing warrants a visit to your doctor. Several pregnancy complications can occur with the placenta. One of the placental pregnancy complications is placenta previa. But before we get into the details of placenta previa, let’s take a look at what the placenta is and what it does for you and your baby during pregnancy.
When the sperm fertilizes the egg, the resulting embryo moves up the fallopian tube and into the uterus where it proceeds to develop into a foetus, the placenta and an amniotic sac. The placenta is actually an organ that will, in time, be the life-support system for your growing baby. It is attached to the wall of the uterus throughout the pregnancy and connected to your baby via the umbilical cord. It will pass out of your body after you have delivered the baby.
The placenta plays the main role in segregating your blood supply from your baby’s blood supply. It is also responsible for nourishing your baby with food and oxygen, eliminating your baby’s waste, and protecting your baby against infections. The placenta is an essential part of any pregnancy. So any problems associated with it should be diagnosed as soon as possible, closely monitored and effectively dealt with.
What is Placenta Previa?
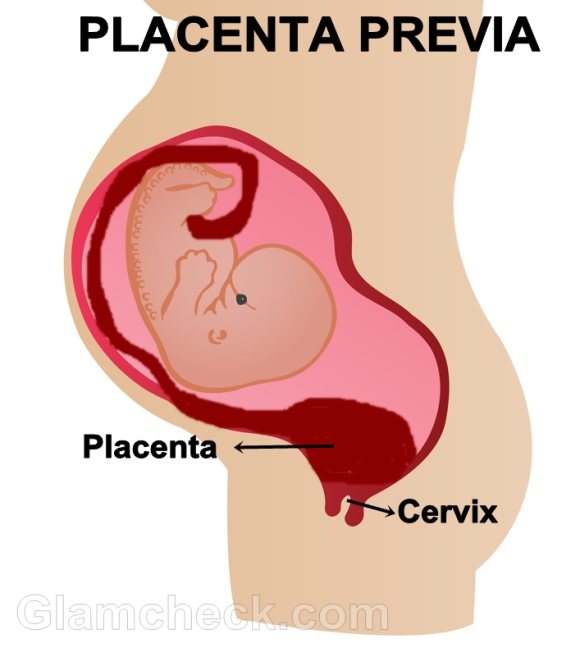 The placenta will develop on the same spot of your uterus where the fertilized egg chose to embed itself. Sometimes, one of the pregnancy complications that occur is that the fertilized egg embeds itself on the lower end of the uterine wall, thus causing the placenta to develop lower too and block the opening of the cervix which is located right below the uterus. In layman’s terms, placenta previa is a low-lying placenta.
The placenta will develop on the same spot of your uterus where the fertilized egg chose to embed itself. Sometimes, one of the pregnancy complications that occur is that the fertilized egg embeds itself on the lower end of the uterine wall, thus causing the placenta to develop lower too and block the opening of the cervix which is located right below the uterus. In layman’s terms, placenta previa is a low-lying placenta.
A low-lying placenta is not always a problem. In most cases, the growth of the uterus will cause it to be pulled along to a higher position which lessens the pregnancy complications arising out of full-fledged placenta previa. If an ultrasound after your 20th pregnancy week shows a low-lying placenta, you will be diagnosed with placenta previa and monitored through the rest of your pregnancy to render appropriate medical treatment.
About one in two hundred women will suffer from placental previa in their pregnancy. But about 20 percent of pregnant women will have placenta previa to a small degree i.e. the placenta is indeed at a lower position on the uterine wall, but not so low as to cause pregnancy complications or be worried about.
Pregnancy Complications of Placenta Previa
In placenta previa, the placenta is either partially or fully blocking the cervical opening, which is your baby’s only route out of your body. If the block is too great, you may have to deliver your baby via caesarean section, not the ideal way to give birth. But there are several other pregnancy complications arising out of placenta previa.
Hemorrhage: If you have placenta previa, one of the pregnancy complications that could arise is painless bleeding that could lead to a haemorrhage, which is fatal for both the mother and the baby. However, the chances of this happening are quite small as if you have been diagnosed with placenta previa then you will be monitored regularly and the severe bleeding will not be allowed to go to a point where it is life-threatening. But in case excessive bleeding does occur, it can be quickly remedied provided you are being treated at a modern medical facility.
Pre-term labor: Having placenta previa has been known to increase the risk of premature labor. And premature labor comes with its own set of complications for the baby like neurological problems, delays in development and learning, blindness, deafness, breathing problems, low birth weight and organ failure. This occurs because the baby has not had enough time in the womb to develop sufficiently to survive in the outside world.
Birth defects: Whether the baby is delivered prematurely or not, there seem to be more birth defects in babies if the mother had placenta previa.
Other placental complications: When you have placenta previa, it increases your risk of placental abruption, which is basically the breaking away of the placenta from the uterine wall. Placenta abruption is one of the more dangerous pregnancy complications for both mother and child. Another placental complication of placenta previa is placenta accreta, which is a case of the placenta being implanted very deeply in the uterus, thus making it harder to separate when the baby is delivered. Placenta accreta can cause hemorrhage, shock, and in rare cases, even death. Placenta previa and placenta accreta seem to go hand in hand in many cases, although it is uncertain which causes which.
Causes of Placenta Previa
Placenta previa occurs when the embryo implants itself on the lower part of the uterine wall in the earliest weeks of pregnancy which can lead to pregnancy complications. So the better question here is, what causes the embryo to implant itself lower instead of higher up in the uterus? Researchers admit that they do not know why this happens, just like with most other pregnancy complications. But they have identified the risk factors associated with placenta previa.
Risk Factors of Placenta Previa
Research has shown that the likelihood of certain pregnancy complications like placenta previa are more likely to occur under the following circumstances.
- If you have had a C-section in an earlier pregnancy, you may have some tissue scarring. The embryo may be more drawn to attach itself to the groove of the scar, thus causing placenta previa.
- As a matter of fact, any kind of surgery that has left a scar on the uterus like a dilation and curettage or a myomectomy has the potential to increase your risk for placenta previa.
- Usually, women over 35 years of age are more likely to develop pregnancy complications like placenta previa.
- Smoking seems to increase the risk factor for placenta previa in addition to other pregnancy complications.
- Women who do cocaine during pregnancy are at higher risk for placenta previa, not to mention a host of other pregnancy complications.
- If you have an abnormally shaped uterus, it can increase your risk of placenta previa.
- Women who are carrying multiple foetuses – twins or triplets or more – are at higher risk of having placenta previa in addition to other pregnancy complications. Researchers hypothesize that this may be so because the placenta has more mouths to feed, so to speak, and thus grows larger to accommodate the extra work it has to do. The growth may sag towards the lower end and partially block the cervical opening.
- There is a higher likelihood of developing placenta previa in your current pregnancy if you suffered from placental pregnancy complications in the past.
- Some research shows that if you have had more than four pregnancies, you are at a higher risk of having placenta previa.
Symptoms of Placenta Previa
Since pregnancy complications like placenta previa have the potential to turn very serious, you must be aware of the symptoms and report to your doctor if you experience them so as to deal with the condition as soon as possible and prevent long-lasting damage.
- You will experience some amount of bleeding in your pregnancy second trimester or pregnancy third trimester if you have placenta previa. It is usually nor accompanied by any pain. But bleeding is an indication of several other pregnancy complications as well so it is not an exclusive symptom of placenta previa although it is a primary one. The bleeding is sometimes recurrent, returning either a few days or a few months after the first time.
- During the first stages of your pregnancy, the baby will be positioned head up. Towards the end of the third trimester, your baby should move upside down, head to cervix in preparation for delivery. If you have placenta previa, the baby may not have enough space to move to the upside-down position. This is called breech position and can cause some pregnancy complications.
- Some women afflicted by placenta previa have also experienced contractions or pain in the lower back or lower abdomen.
Treatment for Placenta Previa
Like most pregnancy complications, placenta previa cannot really be treated, it can only be managed. This is one of those pregnancy complications where you must simply wait and see if the problem fixes itself. Therefore, if you have been diagnosed with placenta previa, you will be asked to take the following precautionary measures.
- You may be asked to not have sex if you have placenta previa.
- Depending on how severe your case of placenta previa is, you may be asked to stop working and take to your bed. Some cases are severe enough that the pregnant mother is admitted to the hospital for round the clock observation.
- No heavy lifting or participating in strenuous activities if you have placenta previa.
- Ensure that you are always around someone who is able to help you with tasks, chores, and who is able to take you to a hospital if something goes wrong. If it is not possible to have someone with you at all times, make arrangements with friends or family to arrive and help at a moment’s notice.
- Women who have placenta previa are normally advised to deliver their babies via C-section between 37 and 38 weeks of pregnancy. Do not worry, your baby will have developed enough by that point to have a good chance of surviving with initial medical care.
- If you are less than 24 weeks pregnant, you will be given medication that will speed up the development of your baby’s lungs so that it can be delivered as soon as possible without pregnancy complications.
- If you experience very heavy bleeding that causes you to go into premature labor, you will have to have the baby by C-section immediately regardless of how many weeks into the pregnancy you are. This is a necessary precaution to save the lived of both you and your baby.
- Your doctor will not even perform vaginal exams if your case is too severe unless he is using special equipment.
If you are diagnosed with placenta previa, you will be called in to see your doctor quite often and have to undergo several ultrasounds to determine the best course of action as your pregnancy progresses.
Prevention of Placenta Previa
You can lower your risk of developing not just placenta previa but other pregnancy complications as well if you quit smoking, do not abuse drugs, eat a nutritious diet that is high in iron, and lead a healthy lifestyle not just when you are pregnant but before and after as well.
Apart from that, just stick to your doctor’s appointments so that if you have placenta previa it can be detected early and you can start taking care of yourself and planning ahead depending on your individual situation.
Image: Shutterstock
