If you are pregnant, then you have probably heard stories from your friends, family, acquaintances or even your doctor about someone else who had pregnancy complications. People love to share medical horror stories, even if they are not part of the story. The unfortunate truth is that most pregnancies will have some pregnancy complications, some serious, some manageable. What’s worse though is that most pregnancy complications cannot even be avoided. An ectopic pregnancy is one of the more serious pregnancy complications which you can do nothing about. Even so, the complications arising out of an ectopic pregnancy are serious enough that you should educate yourself about the condition.
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
When an egg is fertilized by a sperm, it travels into the uterus and implants itself in the uterine wall where it will stay and grow into a baby for the next nine months or so. However, in about 1 of 50 pregnancy cases, the embryo will implant itself to a place other than the uterus. This abnormal implantation is known as an ectopic pregnancy.
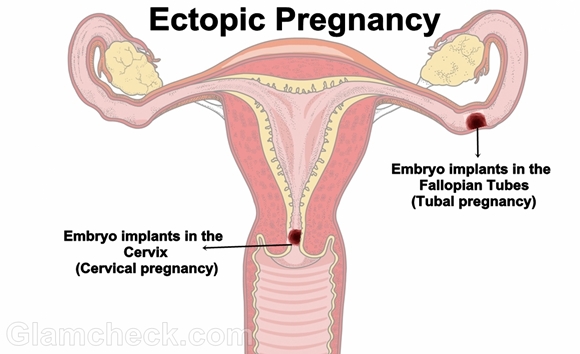 The word ectopic means out of place. In more than 95% of ectopic pregnancy cases, the embryo will implant in the fallopian tubes. That is why an ectopic pregnancy frequently referred to as a tubal pregnancy, although the terms are not inter-changeable.
The word ectopic means out of place. In more than 95% of ectopic pregnancy cases, the embryo will implant in the fallopian tubes. That is why an ectopic pregnancy frequently referred to as a tubal pregnancy, although the terms are not inter-changeable.
Other places that the embryo can implant include the abdomen and the cervix, in which case it will be called an abdominal pregnancy and a cervical pregnancy respectively. The danger to mother and child is no less if the embryo implants in the cervix or abdomen. In extremely rare cases, the embryo can also implant itself in an ovary.
Complications of an Ectopic Pregnancy
There is no space in any other organ but the uterus for the embryo to develop properly. And the other organs are not designed to nourish or safeguard a growing baby. But with an ectopic pregnancy, it will not even get to that point. Besides, an untreated ectopic pregnancy can lead to infertility. So if it is not dealt with immediately, you may never get pregnant again. Or at the very least, you will have a hard time trying to get pregnant. It can take years for your to be successful.
There is great danger to both you and your baby in an ectopic pregnancy. Unfortunately, there is no way to turn this situation around. Your baby will not survive and often does not even develop in an ectopic pregnancy. The embryo cannot, say, be transplanted into the uterus for a normal pregnancy. As for you, the growing embryo will cause the organ it has settled on to burst, leading to excessive bleeding (internal hemorrhage), hypovolaemic shock, and in some cases even death. That is why an ectopic pregnancy is best caught as early as possible so measures can be taken to prevent pregnancy complications from occurring.
Causes of an Ectopic Pregnancy
Researchers have admitted that they are not sure why most pregnancy complications occur. They hypothesize that the ectopic pregnancy may be caused by something blocking or perhaps slowing down the passage of the fertilized egg as it travels from the fallopian tube to the uterus. The blockage could be a result of leftover tissue or scarring from a prior surgery, complications arising from smoking, or pelvic inflammatory disease caused by sexually transmitted diseases like chlamydia or gonorrhea which is known to block the fallopian tubes.
Risk Factors of An Ectopic Pregnancy
The causes of pregnancy complications are hard to pin down. But observation and research can help to identify the groups of women who are at a higher risk of developing certain pregnancy complications. Following are some of the known risk factors of an ectopic pregnancy.
- The number one risk factor for ectopic pregnancies appears to be infection of the reproductive organs.
- Sexually transmitted diseases also put you at a high risk of such pregnancy complications.
- Women who have endometriosis, a condition characterized by the uterine wall growing outside the uterus, may be more susceptible to an ectopic pregnancy.
- If you were exposed to the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) when your mother was pregnant you may be at an increased risk of an ectopic pregnacny.
- You are at a higher risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy if you have had one before.
- Women who smoke are more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy.
- Complications arising from a ruptured appendix can also increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
- Women above 35 years of age seem to be at a higher risk.
- If your method of contraception was to go for tubal ligation – surgically tying off your fallopian tubes – and you get pregnancy anyway, it will probably be an ectopic pregnancy.
- In fact, any surgery on or around the fallopian tubes which may have caused them some damage increases your risk of an ectopic pregnancy. Several women who reverse the tubal ligation in order to get pregnant will have an ectopic pregnancy.
- Some research has shown that women who have unusually-shaped fallopian tubes seem to be at a higher risk for ectopic pregnancy complications.
- Pregnancy that occurs even under the use of contraceptives is most likely to be ectopic.
- Some fertility drugs and treatments have been known to be a risk factor for an ectopic pregnancy.
- A few researchers feel that even douching can be a risk factor for an ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy will progress like a normal pregnancy, with seemingly no pregnancy complications. Your period will stops and you will experience nausea, fatigue, breast tenderness and all the other symptoms related to a normal pregnancy. The symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may be apparent only about a month into the pregnancy. Sometimes, symptoms may not show for up to 3 months. In such a case, however, it will show up on the ultrasound.
If an ectopic pregnancy is not caught early on, you have a lot to lose apart from your baby. It is thus important to educate yourself about the symptoms so that you can call your doctor immediately and further pregnancy complications can be avoided. Here are some of the common and rare symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Vaginal bleeding is the main symptom of an ectopic pregnancy
- It may be accompanied by lower abdominal pain, ranging in intensity from mild to shockingly severe
- Dizziness and/or fainting, especially if experienced along with the symptoms above
- You strongly feel the need to defecate but do not pass any stool
- You may experience pain while urinating
- Pelvic cramping on only one side
- Pain in the lower back
- You may experience pain in or around the shoulders and neck; this happens when a rupture caused by the ectopic pregnancy irritates the nerves
- Low blood pressure
How is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
The symptoms of ectopic pregnancy are quite generic. This means that they can be symptoms for a host of other conditions. So to identify an ectopic pregnancy as the culprit, your doctor will have you undergo the following tests.
- If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, the first thing your doctor will do is give you a pelvic examination to feel for any tenderness in the pelvis, to determine the size of the uterus, and to feel for any abnormal growths where there aren’t supposed to be any.
- A blood test for hCG levels can also be used to diagnose or clarify an ectopic pregnancy. If hCG levels are low for the stage of pregnancy that you are in, then it might indicate an ectopic pregnancy or some other pregnancy complications.
- An ultrasound can show for certain where the pregnancy is developing and if it is developing properly. But a pregnancy cannot be detected until the sixth week, so if you are pregnant for less than 6 weeks, this method will not work to diagnose the ectopic pregnancy. An ultrasound can also show up any internal bleeding.
Treatment for an Ectopic Pregnancy
There is no remedy or cure for an ectopic pregnancy. There is no possible way to turn an ectopic pregnancy into a normal pregnancy. The only option open to you if you are diagnose with an ectopic pregnancy is to terminate the pregnancy to avoid pregnancy complications like infertility and death.
- If you are already quite far along in your ectopic pregnancy, then your doctor will resort to laparoscopic surgery to remove the ectopic tissue. The surgery involves a small incision or two being made on the part of your abdomen that is closest to where the fertilized embryo has implanted itself. A thin tube with a camera, light and other surgical instruments may be passed through the incision to get rid of the ectopic tissue.
- If detected early enough, an ectopic pregnancy can be terminated with an injection of methotrexate, a drug that will prevent the cells from growing and dividing further, and dissolve any existing cells. After you have been given an injection of the drug, the hCG (pregnancy hormones) levels in your blood will be monitored. If they do not go down, you may be given another injection of the drug. This method of treatment can only be used if no damage has been done to the fallopian tubes yet as a damaged fallopian tube must be removed to prevent further complications.
- In case of very heavy bleeding which can cause death of the mother, emergency open surgery (laparotomy) may be required.
- If your fallopian tubes are too damaged to be repaired by surgery, they will have to be removed. Sometimes, only one side of the tubes need to be removed. In such a case, it is still possible to get pregnant again as the sperm can travel up the other fallopian tube and fertilize the egg before moving on to the uterus.
Can an Ectopic Pregnancy be Prevented?
Unfortunately not. There is nothing you can do to prevent ectopic pregnancy or even to reduce your chances of having an ectopic pegnancy. But if you can prevent certain risk factors, you may have a fighting chance of preventing the pregnancy complications of an ectopic pregnancy.
For example, you can keep your sexual partners during pregnancy to a minimum. Multiple sexual partners increase your chances of an infection or an STD which, as we have seen, are a couple of the leading risk factors for an ectopic pregnancy. You can also stop smoking to increase your chances of a normal pregnancy with no complications. In fact, smoking is a risk factor for several pregnancy complications and it is bad for health to boot; so you could stop it overall, not just during pregnancy.
Remember to stick to your doctor’s appointments so that pregnancy complications can be caught early on. And rest assured though that many women who get their ectopic pregnancies diagnosed and treated early enough have gone on to get pregnant again and have had normal pregnancies with no complications.
Image: Shutterstock
