Understanding menstruation:
Menstruation is a woman’s monthly bleeding, also called a period or menses. The bleeding happens when the thickened uterine lining (endometrium) sheds. During menstruation, the menstrual blood flows from the uterus through the small opening in the cervix, and passes out of the body through the vagina.
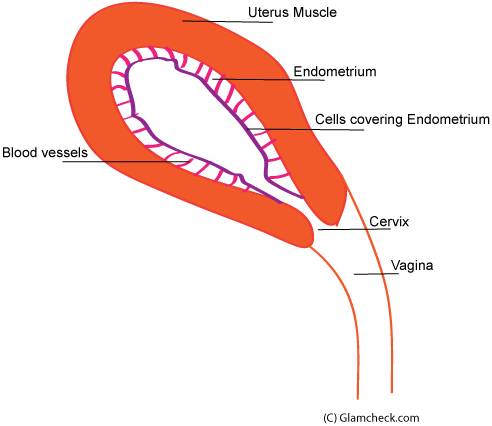
- The endometrium is thin immediately after the menstrual bleeding has stopped.
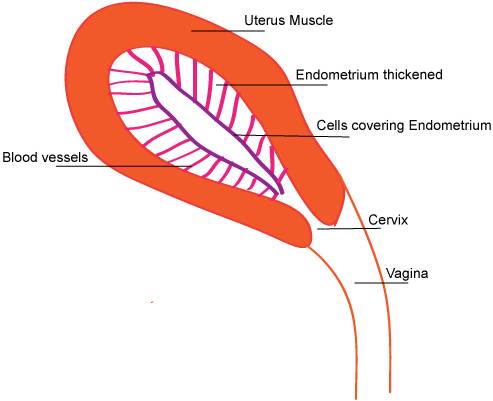
- The endometrium (about one week later). It is now much thicker.
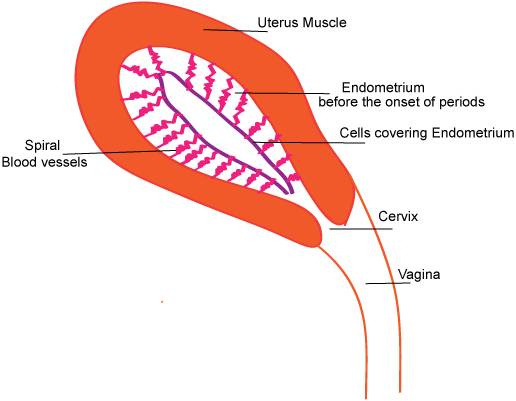
- The endometrium immediately before the onset of menstruation. Appearance of spiral blood vessels.
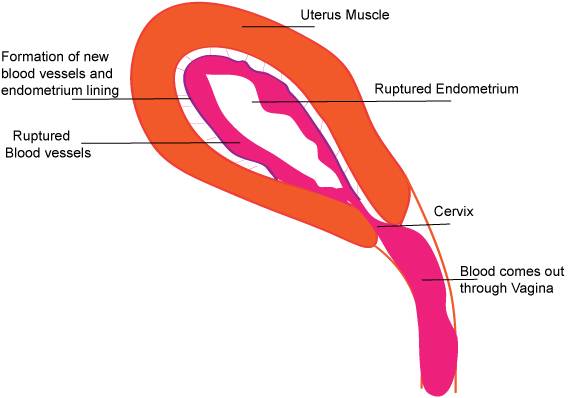
- Menstruation starts. The Endometrium is broken. The blood vessels are exposed and ruptured and bleeding starts. The blood comes out through the vagina. Anticoagulants prevent the blood clotting.
- At the same time, the uterus starts preparing itself for the next cycle by developing another endometrium.
Menstruation is part of the menstrual cycle. The average menstrual cycle lasts 28 days. For some women, the cycles may vary and can be as short as 21 days or can be as long as 35 days.
Menstruation can be light, moderate, or even heavy. For how many days the periods will last also varies. A normal period lasts between 2 to 7 days. Usually, the flow of the menstrual blood is more during the first 2 days of the start and gradually slows before it ends.
Menstrual Blood Problems: Color, flow, odor and thickness
Menstrual blood Color
The color of the menstrual blood depends on bleeding rate. Slow bleeding results in darker menstrual blood.
During the first 2 days of the onset of the periods, one may see deep red color blood coming out. Whereas, the color changes to dark brown or even black near the end of the periods. This is absolutely a normal color change that happens when the blood is older and not being expelled from the body quickly. During the first 2 days, the blood comes out rapidly and therefore appears red in color. Whereas, during the 3rd ,4th and 5th day, it changes to dark brown or black color because the blood component loses its oxygenated red hue due to its long stay in the uterus. The color of menstrual blood can vary month to month.
The amount of blood and fluid lost is usually between 5 and 12 teaspoons each cycle.
- Narrow cervical opening may cause change in menstrual blood color
However, if associated with severe cramping, this brown / black blood may be a sign that the cervical opening is too narrow, preventing free flow of menstrual blood. In this case, the blood stays in the uterus for a while, until contractions of the uterus push it out. This calls for a visit with your gynecologist.
- Endometriosis may cause change in menstrual blood color
If you are experiencing pain in your pelvis, painful periods and pain during intercourse, you could be suffering from endometriosis. The tissue lining the uterus grows outside of the uterus instead of growing inside, causing discomfort and a darker discharge during periods.
- Infection may cause change in menstrual blood color
Darker menstrual blood can also be a result of an infection or a sexually transmitted disease. If you experience an unusual abdominal tenderness and fever along with a dark blood discharge with a foul odor you are advice to see a gynecologist.
Menstrual blood odor:
- Menstrual blood does not smell bad and is neither dirty. However, it only tends to have an unpleasant odor after it has been in contact with air for a period of time.
- Sometimes an infection can also cause menstrual blood to look and smell bad. If the smell is hard to be tolerable associated with severe cramping, fever, heavy flow with thicker blood clots, you need to see your gynecologist.
Thick and heavy menstrual flow:
- Temporary thick and heavy flow isn’t a cause for concern. However, regular heavy periods call for a trip to the doctor to check your blood counts. Over the time, the excess monthly blood loss leads to anemia, causing weakness or fatigue.
- Heavy periods may also be due to the presence of fibroids or non-cancerous tumors of the uterus.
- Heavy or prolonged periods are called dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB). DUB includes hormonally-caused bleeding abnormalities or bleeding disorders. These bleeding abnormalities require medical attention.
